Article
Frank Slide
At 4:10 AM on 29 April 1903, 74 million tonnes of rock crashed down the east slope of Turtle Mountain in the Crowsnest Pass region of Alberta

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
At 4:10 AM on 29 April 1903, 74 million tonnes of rock crashed down the east slope of Turtle Mountain in the Crowsnest Pass region of Alberta
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/698e80ed-51d4-40c7-a75f-36d14b5e66b3.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/698e80ed-51d4-40c7-a75f-36d14b5e66b3.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
The Fraser River Canyon was formed during the Miocene period (22.9-5.33 million years ago) when the river cut down into the uplifting southern part of the Interior Plateau of British Columbia. The canyon characteristics of this
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/49e5b82d-d0a2-4ca6-aa37-99ecf1243a3d.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/49e5b82d-d0a2-4ca6-aa37-99ecf1243a3d.jpg

Article
In 1858, around 30,000 gold seekers flooded the banks of the Fraser River from Hope to just north of Lillooet in British Columbia’s first significant gold rush. Although it dissipated by the mid-1860s, the Fraser River Gold Rush had a significant impact on the area’s Indigenous peoples and resulted in the Fraser Canyon War. Fears that the massive influx of American miners would lead the United States to annex the non-sovereign British territory known as New Caledonia also resulted in the founding of British Columbia as a colony on 2 August 1858 (see The Fraser River Gold Rush and the Founding of British Columbia). By the mid-1860s, the Fraser Rush collapsed, and British Columbia sank into a recession.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/FraserCanyonWar/Fraser Canyon near Chapmans Bar, Daniel Marshall(1).jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/FraserCanyonWar/Fraser Canyon near Chapmans Bar, Daniel Marshall(1).jpg
.jpg)
Article
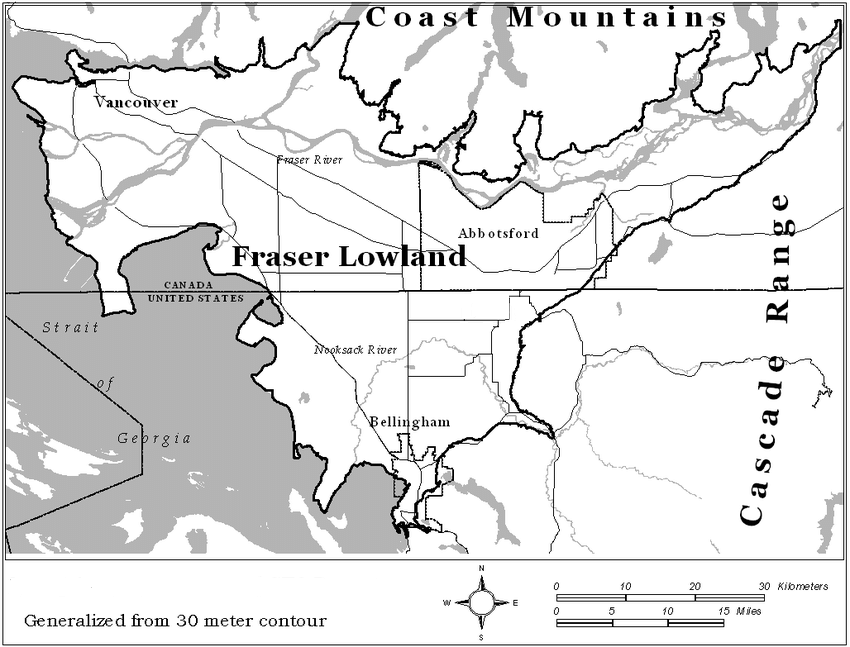
The Fraser River Lowland is a triangular area in southwestern British Columbia. The eastern apex of the triangle is at Hope, about 160 km inland from the Strait of Georgia. From here, the lowland broadens to the west to a width of about 50 km. The international boundary between British Columbia and Washington State crosses the southwestern part of the lowland. The Coast Mountains form the northern boundary of the delta-lowland. The Fraser River Lowland is the largest area of level land with suitable agricultural soils in coastal British Columbia.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/FraserRiverLowland/FraserRiverLowlandMap.png" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/FraserRiverLowland/FraserRiverLowlandMap.png
Article
The Freshwater Institute, located on the University of Manitoba campus in Winnipeg, Man, is one of the world's leading research centres for freshwater and Arctic fisheries research.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/8ff204ea-7793-42b9-9f34-39964ccf0d12.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/8ff204ea-7793-42b9-9f34-39964ccf0d12.jpg

Macleans
"I don't understand. Is this a loaded question?" The line of query had not been terribly abstract.This article was originally published in Maclean's Magazine on September 9, 1996
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Frogs are amphibians belonging to the order Anura. Worldwide, frogs are the most numerous group of amphibians, with more than 5,000 living species. They are found on all continents except Antarctica. There are 24 species of frog currently found in Canada. In addition, one species, the Blanchard’s cricket frog, is extirpated. This means that, while it continues to live in other parts of its range, it is no longer found in Canada. Five of Canada’s frog species are toads, which are frogs belonging to the family Bufonidae. While most frog species in Canada are found in the southern reaches of the country, a few, for example the boreal chorus frog, have ranges extending into Yukon and the Northwest Territories, and in the case of the wood frog, Nunavut.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/FrogSpeciesInCanada/AmericanBullfrog.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/FrogSpeciesInCanada/AmericanBullfrog.jpg

Article
This important sector of Canada's FOOD AND BEVERAGE INDUSTRIES is made up of companies that process fruits and VEGETABLES.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/c5d66760-a348-43b1-af55-7b9263c442cb.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/c5d66760-a348-43b1-af55-7b9263c442cb.jpg

Article
Fruit growing is an important part of Canada’s food industry. Growing is usually restricted to areas where winter temperatures do not go much below -20°C.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/a2ab80b2-d4e9-4e51-aef5-dd1615e358f8.JPG" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/a2ab80b2-d4e9-4e51-aef5-dd1615e358f8.JPG

Article
All members of the kingdom Fungi are commonly known by the same name, fungus. Fungi have some characteristics in common with both plants and animals, yet they are an independent group. Plants, animals and fungi are thought to have a common ancestor, probably a simple eukaryotic (cells having distinct nuclei) organism highly unlike its modern descendants. Evidence suggests that fungi and animals are more closely related to each other than either is to plants. Like animals, all fungi lack chlorophyll and cannot carry out photosynthesis.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/fungus/Decorated-Mop.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/fungus/Decorated-Mop.jpg

Article
The fur trade began in the 1600s in what is now Canada. It continued for more than 250 years. Europeans traded with Indigenous people for beaver pelts. The demand for felt hats in Europe drove this business. The fur trade was one of the main reasons that Europeans explored and colonized Canada. It built relationships between Europeans and Indigenous peoples. (This article is a plain-language summary of the fur trade. If you are interested in reading about this topic in more depth, please see our full-length entry, Fur Trade in Canada.)
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/article_files/fur-trade/c002771k.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/article_files/fur-trade/c002771k.jpg

Article
Gallinule is a common name for some marsh-dwelling birds of the rail family (Rallidae), now also known as moorhens.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/7a9dff00-31fa-400c-910d-dbc148c48f73.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/7a9dff00-31fa-400c-910d-dbc148c48f73.jpg

Article
Game bird is not a scientific term, but refers to any bird that is hunted. There are 2 categories in Canada, migratory and nonmigratory.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/82572582-06cb-4165-a0ba-fbb3f8e521d1.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/82572582-06cb-4165-a0ba-fbb3f8e521d1.jpg

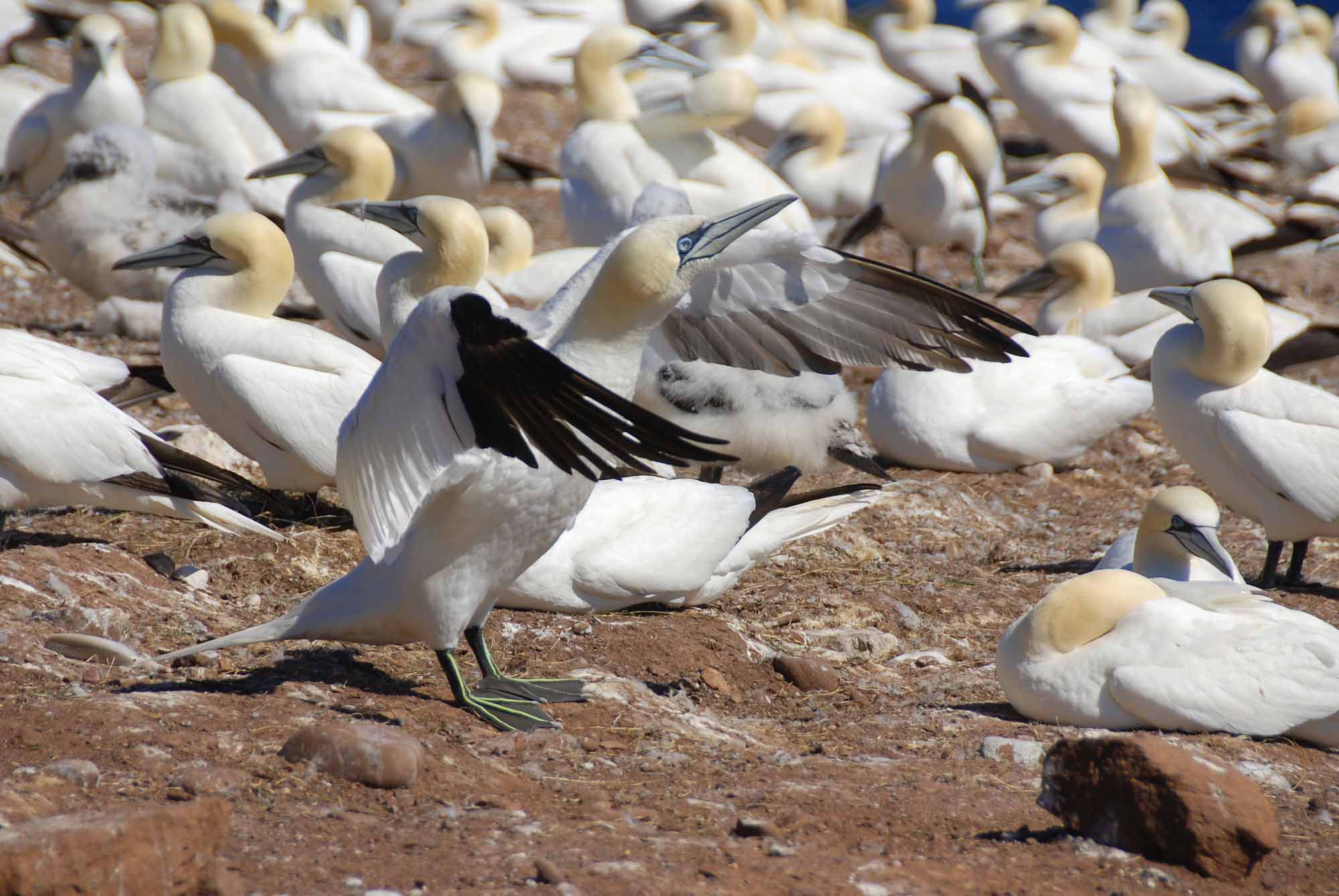
Article
The gannet, or northern gannet (Sula bassanus) is a large, long-winged seabird, white except for conspicuous black wing tips and yellowish tinged head.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/b2be0d1b-9e0f-4794-997a-2ec03cbfab51.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/b2be0d1b-9e0f-4794-997a-2ec03cbfab51.jpg
